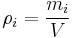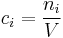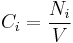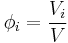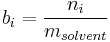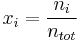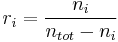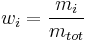Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Furthermore, in chemistry, four types of mathematical description can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration.[1] The term concentration can be applied to any kind of chemical mixture, but most frequently it refers to solutes in homogeneous solutions.
Contents |
Qualitative description
Often in informal, non-technical language, concentration is described in a qualitative way, through the use of adjectives such as "dilute" for solutions of relatively low concentration and "concentrated" for solutions of relatively high concentration. To concentrate a solution, one must add more solute (for example, alcohol), or reduce the amount of solvent (for example, water). By contrast, to dilute a solution, one must add more solvent, or reduce the amount of solute. Unless two substances are fully miscible there exists a concentration at which no further solute will dissolve in a solution. At this point, the solution is said to be saturated. If additional solute is added to a saturated solution, it will not dissolve, except in certain circumstances, when supersaturation may occur. Instead, phase separation will occur, leading to coexisting phases, either completely separated or mixed as a suspension. The point of saturation depends on many variables such as ambient temperature and the precise chemical nature of the solvent and solute.
Quantitative notation
There are four quantities that describe concentration:
Mass concentration
The mass concentration 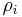 is defined as the mass of a constituent
is defined as the mass of a constituent 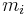 divided by the volume of the mixture
divided by the volume of the mixture 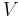 :
:
The SI-unit is kg/m3.
Molar concentration
The molar concentration 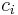 is defined as the amount of a constituent
is defined as the amount of a constituent 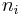 divided by the volume of the mixture
divided by the volume of the mixture 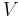 :
:
The SI-unit is mol/m3. However, more commonly the unit mol/L is used.
Number concentration
The number concentration 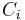 is defined as the number of entities of a constituent
is defined as the number of entities of a constituent 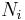 in a mixture divided by the volume of the mixture
in a mixture divided by the volume of the mixture 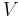 :
:
The SI-unit is 1/m3.
Volume concentration
The volume concentration 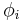 (also called volume fraction) is defined as the volume of a constituent
(also called volume fraction) is defined as the volume of a constituent 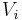 divided by the volume of all consituents of the mixture
divided by the volume of all consituents of the mixture 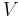 prior to mixing:
prior to mixing:
The SI-unit is m3/m3.
Related Quantities
Several other quantities can be used to describe the composition of a mixture. Note that these should not be called concentrations.
Normality
Normality is defined as the molar concentration 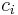 divided by an equivalence factor
divided by an equivalence factor 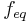 . Since the definition of the equivalence factor may not be unequivocal, IUPAC and NIST discourage the use of normality.
. Since the definition of the equivalence factor may not be unequivocal, IUPAC and NIST discourage the use of normality.
Molality
The molality of a solution 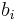 is defined as the amount of a constituent
is defined as the amount of a constituent 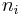 divided by the mass of the solvent
divided by the mass of the solvent 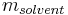 (not the mass of the solution):
(not the mass of the solution):
The SI-unit for molality is mol/kg.
Mole fraction
The mole fraction 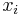 is defined as the amount of a constituent
is defined as the amount of a constituent 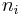 divided by the total amount of all constituents in a mixture
divided by the total amount of all constituents in a mixture 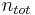 :
:
The SI-unit is mol/mol. However, the deprecated parts-per notation is often used to describe small mole fractions.
Mole ratio
The mole ratio 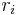 is defined as the amount of a constituent
is defined as the amount of a constituent 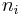 divided by the total amount of all other constituents in a mixture:
divided by the total amount of all other constituents in a mixture:
If 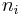 is much smaller than
is much smaller than 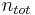 , the mole ratio is almost identical to the mole fraction.
, the mole ratio is almost identical to the mole fraction.
The SI-unit is mol/mol. However, the deprecated parts-per notation is often used to describe small mole ratios.
Mass fraction
The mass fraction 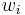 is the fraction of one substance with mass
is the fraction of one substance with mass 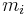 to the mass of the total mixture
to the mass of the total mixture 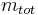 , defined as:
, defined as:
The SI-unit is kg/kg. However, the deprecated parts-per notation is often used to describe small mass fractions.
Mass ratio
The mass ratio 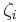 is defined as the mass of a constituent
is defined as the mass of a constituent 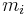 divided by the total mass of all other constituents in a mixture:
divided by the total mass of all other constituents in a mixture:
If 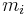 is much smaller than
is much smaller than 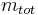 , the mass ratio is almost identical to the mass fraction.
, the mass ratio is almost identical to the mass fraction.
The SI-unit is kg/kg. However, the deprecated parts-per notation is often used to describe small mass ratios.
Dependence on volume
Concentration depends on the variation of the volume of the solution due mainly to thermal expansion.
| Concentration type | Symbol | Definition | SI-unit | other unit(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mass concentration | 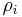 or or 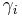 |
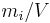 |
kg/m3 | g/100mL (=g/dL) |
| molar concentration | 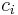 |
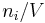 |
mol/m3 | M (=mol/L) |
| number concentration | 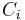 |
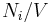 |
1/m3 | 1/cm3 |
| volume concentration | 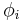 |
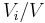 |
m3/m3 | |
| Related quantities | Symbol | Definition | SI-unit | other unit(s) |
| normality | 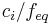 |
mol/m3 | M (=mol/L) | |
| molality | 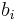 |
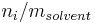 |
mol/kg | |
| mole fraction | 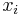 |
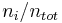 |
mol/mol | ppm, ppb, ppt |
| mole ratio | 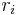 |
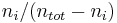 |
mol/mol | ppm, ppb, ppt |
| mass fraction | 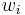 |
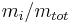 |
kg/kg | ppm, ppb, ppt |
| mass ratio | 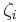 |
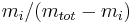 |
kg/kg | ppm, ppb, ppt |
See also
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "concentration".
|
||||||||||||||